What is Glutathione and How Can You Increase Your Levels?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Glutathione is a term that’s becoming more common in health circles, and for good reason. Often referred to as the “master antioxidant,” glutathione plays a crucial role in maintaining our health and protecting our cells from damage. But what exactly is glutathione, and why is it so important? More importantly, how can we ensure our bodies have enough of it? Let’s dive into the details.
What is Glutathione?
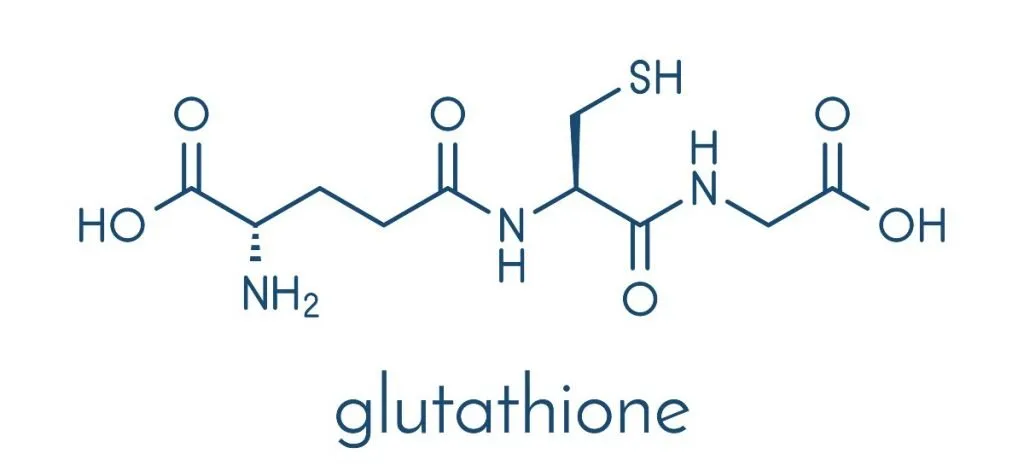
At its core, glutathione is a small protein composed of three amino acids: glutamine, cysteine, and glycine. This powerful antioxidant is naturally produced in the liver and is present in every cell of the body. Glutathione’s primary function is to neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases. It’s also vital for various metabolic processes, including DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and enzyme activation.
The Importance of Glutathione
Glutathione isn’t just any antioxidant; it’s pivotal to your health for several reasons:
Antioxidant Properties: As the body’s primary antioxidant, glutathione neutralizes free radicals and protects cells from oxidative stress, a key factor in aging and many diseases.
Detoxification: Glutathione plays a crucial role in detoxifying the liver, helping to eliminate toxins and heavy metals from the body.
Immune System Support: It supports the immune system by maintaining the function of lymphocytes, white blood cells that are essential for immune defense.
Cellular Repair: Glutathione aids in the repair and regeneration of cells, helping to maintain overall cellular health.
How Glutathione Works in the Body
Understanding how glutathione works gives us insight into why it’s so vital:
Oxidative Stress Management: Glutathione scavenges free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage.
Liver Function and Detoxification: Glutathione binds to toxins, facilitating their excretion from the body, particularly in the liver.
Skin Health: Glutathione contributes to skin brightening by inhibiting melanin production, which can reduce the appearance of dark spots.
DNA Synthesis and Repair: It assists in the synthesis and repair of DNA, ensuring the proper functioning and reproduction of cells.
Factors That Decrease Glutathione Levels
Several factors can lead to a decrease in glutathione levels, including:
Aging: As we age, our body’s ability to produce glutathione naturally decreases.
Poor Diet: Lack of nutrients, particularly those that are glutathione precursors like cysteine, can reduce glutathione levels.
Exposure to Toxins: Environmental pollutants, smoking, and alcohol consumption can deplete glutathione as the body uses it to detoxify these substances.
Chronic Stress: Persistent stress can increase the body’s demand for glutathione, leading to depletion.
Illness and Infection: During illness or infection, the body may require more glutathione to fight off pathogens, which can lower its levels.
Symptoms of Low Glutathione Levels
When glutathione levels drop, you might notice a variety of symptoms:
Fatigue and Weakness: Low glutathione can lead to decreased energy levels and chronic fatigue.
Frequent Illnesses: A weakened immune system may result in more frequent colds or infections.
Skin Issues: Dryness, discoloration, or a dull complexion can be signs of low glutathione.
Increased Oxidative Stress: Without enough glutathione, oxidative stress can increase, leading to inflammation and potential damage to cells.
Cognitive Decline: Some studies suggest that low glutathione levels may be linked to memory issues or cognitive decline.
How to Naturally Increase Glutathione Levels
Fortunately, there are several ways to boost your glutathione levels naturally:
Dietary Approaches
Foods Rich in Glutathione: Incorporate foods like spinach, avocados, and asparagus, which are naturally high in glutathione.
Sulfur-Rich Foods: Foods like garlic, onions, and cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts) are rich in sulfur, a key component of glutathione.
Selenium-Rich Foods: Selenium, found in Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds, and fish, is essential for glutathione production.
Vitamins C and E: These vitamins help to recycle glutathione and enhance its effectiveness in the body. Citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds are excellent sources.
Supplements for Boosting Glutathione
Glutathione Supplements: Direct glutathione supplements can be taken, though their effectiveness is debated since glutathione may be broken down in the digestive tract before absorption.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC): This supplement is a precursor to glutathione and is widely recognized for its role in boosting glutathione levels.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): ALA can help regenerate glutathione and is available in supplement form.
Whey Protein: High in cysteine, whey protein can support the body’s production of glutathione.
Lifestyle Changes
Regular Exercise: Exercise has been shown to increase glutathione levels, particularly when combined with a healthy diet.
Stress Management: Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress, preserving your glutathione levels.
Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get enough sleep each night is crucial for maintaining healthy glutathione levels.
Reducing Exposure to Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, including smoking and alcohol, to help maintain your glutathione levels.
Medical Treatments to Increase Glutathione
For those who need a more significant boost, medical treatments are available:
Intravenous (IV) Glutathione Therapy: Administering glutathione directly into the bloodstream can increase levels more effectively than oral supplements.
Glutathione Injections: These are often used in clinical settings to quickly elevate glutathione levels.
Liposomal Glutathione: This form of glutathione is encapsulated in liposomes, which may improve absorption and effectiveness.
Risks and Side Effects of Excess Glutathione
While boosting glutathione is generally beneficial, there are risks to over-supplementation:
Potential Risks: Excessive glutathione can lead to gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions in some people.
Balancing Levels: It’s important to find the right balance, particularly if using supplements or medical treatments.
Who Should Avoid It?: People with certain conditions, such as asthma, should consult with a healthcare provider before using glutathione supplements.
Myths and Misconceptions About Glutathione
There’s a lot of misinformation about glutathione, particularly regarding its role in skin lightening:
Debunking Myths: Glutathione is not a magic bullet for all health issues, and its effectiveness can vary based on how it’s used.
Skin Lightening Misconceptions: While glutathione is popular in some regions for skin lightening, the science behind its effectiveness for this purpose is still unclear.
Glutathione and Skin Health
Glutathione is often touted for its skin benefits:
Skin Brightening and Anti-Aging: Glutathione’s antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress, which can lead to brighter, more youthful-looking skin.
Acne Treatment: Some studies suggest that glutathione can help reduce acne by decreasing inflammation.
Hyperpigmentation: Glutathione may help reduce hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanin production, but results can vary.
Glutathione and Athletic Performance
Athletes may also benefit from optimal glutathione levels:
Muscle Recovery: Glutathione helps in reducing muscle damage and speeding up recovery post-exercise.
Oxidative Stress: By reducing oxidative stress, glutathione can improve endurance and performance.
Athletic Benefits: Ensuring adequate glutathione levels can support overall physical performance and recovery.
Glutathione in Chronic Diseases
Glutathione’s role in managing chronic diseases is an area of ongoing research:
Chronic Diseases: Conditions like diabetes and cancer may be linked to low glutathione levels, making supplementation or enhancement beneficial.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Studies suggest glutathione may play a role in protecting against diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Therapeutic Uses: Research is ongoing into how glutathione can be used therapeutically in chronic conditions.
Future Research and Developments
The potential of glutathione is far from fully understood:
Emerging Studies: New research continues to explore glutathione’s benefits and applications.
Future Applications: As our understanding grows, glutathione could play a role in treating a variety of conditions.
Ongoing Research: Scientists are investigating new ways to enhance glutathione levels and its effectiveness in disease prevention and treatment.
Conclusion
Glutathione is an essential antioxidant that plays a critical role in maintaining overall health. From detoxification to immune support, this powerful molecule is vital for our well-being. By incorporating glutathione-boosting strategies such as a nutrient-rich diet, proper supplementation, and healthy lifestyle choices, you can help ensure that your glutathione levels remain optimal, supporting your body’s natural defense mechanisms.
FAQs
Can glutathione help with weight loss?
- Glutathione is not directly linked to weight loss, but by supporting overall cellular health and detoxification, it may contribute to a more balanced metabolism.
Is it safe to take glutathione every day?
- For most people, daily glutathione supplements are safe, but it’s best to consult a healthcare provider to determine the right dosage.
How long does it take to see the effects of increased glutathione?
- The time it takes to see effects can vary depending on the method of supplementation and individual health conditions, but many people notice improvements within a few weeks.
Can glutathione supplements cause any side effects?
- While generally safe, some people may experience mild side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions.
What is the best way to increase glutathione levels naturally?
- A combination of a nutrient-rich diet, regular exercise, and managing stress is the most effective way to naturally increase glutathione levels.
-
Vitamin Drips
Glutanex Glutathione 1200mg IV Drip for Antiaging, Melanin Suppression, Antioxidant Skin Brightness Benefits
£20.00 – £120.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageRated 0 out of 5 -
Vitamin Drips
Asconex Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) IV Drip for Antiaging, Melanin Suppression, Antioxidant and Skin Brightness Benefits
£10.00 – £70.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageRated 0 out of 5 -
Vitamin Drips
Kosdaq Vitamin D 300000 IU Cholecalciferol per vial box of 10 ampoules
£20.00 – £140.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageRated 0 out of 5
Checkout our Facebook Page and leave your review about our Health Care Products.






